外来でいただく質問で多いものが、「どうして関節リウマチになったんですか?」という質問です。関節リウマチの発症には、遺伝的要因と環境的要因の相互作用が関わっています。
その中で、明確にリスクと分かっているものの一つが、喫煙です。
このページでは、関節リウマチと喫煙についてまとめました。
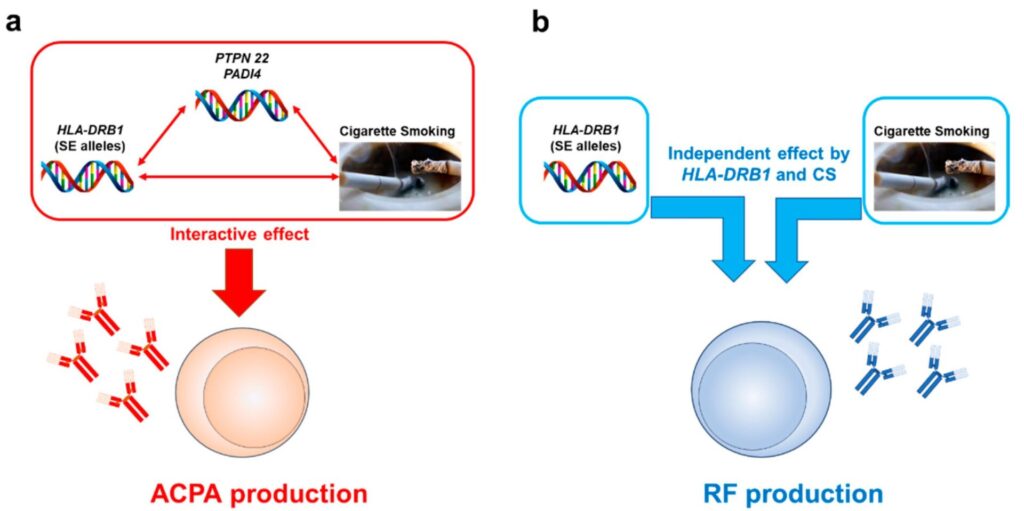
喫煙は、抗CCP抗体(ACPA)やリウマチ因子(RF)を作りやすく、リウマチ発症のリスクをあげます。
これまでの研究で、関節リウマチ発症や関節リウマチの自己抗体産生のリスクとして、いくつかの遺伝的・環境的因子が示されており、その中でも、タバコとHLA-DRB1は、それぞれ確立された環境リスクと遺伝的リスクと考えられています。
今回、CELLの論文が関節リウマチと喫煙のエビデンスがまとまっていたため、紹介します。
First Authors Study Type Outcomes Effects and Effect Sizes Interaction between CS and Genetic Components Stratifications Population, Country, Study Period Di Giuseppe Meta-analysis RF (+) or (−) RA development Dose-dependent increase of RR (1.26–2.07) up to 40 pack-years; RR 2.47 and 1.58 for RF (+) and (−) RA, respectively
(関節リウマチの発症を1.26倍~2.07倍増やす)NA Pack-years; RF Three cohorts and seven case-control studies; a total of 4552 RA cases Hedström Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA development OR 1.9 and 1.3 for ACPA (+) and (−) RA, respectively; a dose-response association (p for trend < 0.0001); cessation > 20 years diminishes the risk of ACPA (−) RA
抗CCP抗体を作りやすいNA Never-, ever-, past, current smokers; duration; intensity; pack-years; ACPA 3655 cases and 5883 matched controls in Sweden Hedström Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA development No association between passive smoking and RA risk (OR ~ 1.0 for both ACPA (+) and (−) RA)
受動喫煙は発症リスクと相関しなかったNA Duration of exposure; ACPA 589 cases and 1764 controls without smoking history Seror cohort RA development Only a suggestive risk of passive smoking (HR1.4–1.7) 受動喫煙のリスクはSuggestive risk程度
NA Never- or ever-smokers w/or w/o passive CS during childhood 71,248 French female volunteers prospectively followed since 1990; 371 RA cases Kim intra-case Clinical response Better clinical response in never-smokers than in passive smokers 非喫煙者の方が受動喫煙者より臨床的な改善がよい
NA Never, current, ex-, and passive smokers 191 female RA cases in South Korea Torrente-Segarra intra-case Clinical response Better clinical response in never- than in passive smokers, which does not result in better drug survival 非喫煙者の方が受動喫煙者より臨床的な反応がよかった、薬の離脱率は変わりなかった
NA Smoking status, ACPA 1349 RA cases from METEOR database between 2006 and 2016 Rydell intra-case Radiographic progression OR 3.17 for RRP in ever-smokers
喫煙者の方がレントゲンの進行が強かったNA Never-, current, ever-, and previous smokers 233 early RA cases during 1995–2005 in Sweden Sivas intra-case Disease activity, radiographic score Higher erosion and joint space narrowing scores in smokers; no correlation of smoking with disease activity 喫煙者でレントゲンの進行が強かった
NA Never-, long-term, and new smokers 165 Turkish RA cases (129 females) followed between January 2015 and February 2016 van Wesemael Case-control RF, ACPA, and anti-CarP Ab presence Smoking was associated with multiple autoantibody positivity both in non-RA and RA cases (OR 1.32–2.95) 自己抗体発生が喫煙者で多かった
NA Never- and ever-smokers; ACPA, RF, anit-CarP Ab 9575 Japanese non-RA subjects; early RA cases from the Netherlands (n = 678), UK (n = 761), and Sweden (n = 795) Ishikawa intra-case RF or ACPA positivities and levels OR of CS 2.06 and 1.29 for high levels of RF and ACPA, respectively リウマチ因子や抗CCP抗体が喫煙者で多かった
Interactive effect of CS and SE on ACPA levels but not those of RF Never-smokers, ex- or active smokers at the onset; SE; ACPA; RF 6239 Japanese RA cases Klareskog Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA development Dose-dependent effect of CS on ACPA (+) RA development 喫煙量が多いほど抗CCP抗体陽性や関節リウマチ発症が多かった
Interactive effect between CS and SE on ACPA (+) RA Never and ever-smokers; pack-years; numbers of SE; RF; ACPA 913 early RA cases and 1357 controls, Sweden Too Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA development OR of CS 4.1 and OR of SE 4.7 for ACPA (+) RA development 喫煙者で4.1倍抗CCP抗体陽性の関節リウマチになりやすかった
Interactive effect between CS and SE on ACPA (+) RA Never- and ever-smokers; SE; ACPA; RF 1076 early RA cases and 1612 matched controls, Malaysia, 2005–2009 Lee intra-case ACPA (+) or (−) RA development Correlation between CS and ACPA (+) RA was observed in 2 out 3 cohorts. 抗CCP抗体陽性と喫煙の関係がみられた
Weak interaction between CS and SE for ACPA only in one cohort Never- and ever-smokers; SE; ACPA; RF A total of 2476 white patients with RA from three different cohorts, North America Bang Case-control ACPA or RF (+) or (−) RA development OR of ever-smoking 2.22 for ACPA (+) and 2.80 for ACPA (−) RA 喫煙歴があると、抗CCP抗体陽性、陰性いずれの関節リウマチも多かった
Interactive effect of CS and SE both on ACPA (+) and ACPA (−) subsets Never- and ever-smokers; SE; DRB1*09:01; ACPA; RF 1482 RA cases and 1119 control subjects, Korea Murphy intra-case ACPA or RF (+) or (−) RA development Strong association between ACPA and RF but not ACPA and CS; no association of CS and ACPA in RF (−) cases No interaction between CS and SE Never- and ever-smokers; Pack-years; SE; ACPA; RF Two different UK RA cohorts (n = 658 and 409) van der Helm-van Mil cohort ACPA (+) or (−) RA development HLA–DRB1*0401, *0404, *0405, or *0408 SE alleles conferred the highest risk of ACPA development HLA–DRB1*0401, *0404, *0405,などの遺伝的背景の患者では、喫煙と抗CCP抗体発生のリスクが高かった
Strongest interaction between CS and *01:01 or *01:02 and *10:01 alleles Current and past smokers; SE and subsets; ACPA 977 undifferentiated arthritis cases, Netherland Pedersen Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA development No significant effect of CS on SE (−) subjects ACPA陰性患者では、大きな関係はなかった。
Strong interaction between CS and SE for ACPA (+) but not ACPA (−) RA SE; ACPA; never- and ever-smokers; pack-years; coffee or alcohol consumption; oral contraceptive use 445 RA cases and 533 age- and sex-matched controls, Denmark, 2002–2004 Padyukov Case-control RF (+) or (−) RA development Neither CS nor SE genes nor the combination increased the risk of RF (−) RA development Significant interaction between CS and any SE genes on RF (+) RA Gender, smoking status, and HLA-DRB1 genotypes, RF RA 858 cases and 1048 controls recruited during 1996 to 2001, Sweden Mattey intra-case RF (+) or (−) RA development OR of ever-smoker for RF (+) RA development 2.2 in ever-smokers independent effects of CS and SE, HLA-DRB1*04:01, on RF (+) RA Never-, ever-, current smokers; SE and subsets; RF 371 RA cases, UK Hedström Case-control ACPA or RF (+) or (−) RA development An independent effect of CS on RF (+) but not on RF (−) RA regardless of ACPA status
リウマチ因子陽性者では、喫煙は独立した関節リウマチ発症リスクだった。Significant interaction between CS and SE on ACPA (+) RA Never-, ever-, current smokers; SE; ACPA, RF 3645 cases, 5883 matched controls, Sweden; follow-up on Ref. 17 Lundström Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA development Lack of an independent effect of CS on ACPA (+) RA Significant interaction of CS with all SE genes tested on ACPA (+) RA Never- or ever-smokers; SE (DRB1*04, *01, and *10); ACPA RA 1319 cases and 943 controls recruited during 1996 to 2005, Sweden; partially overlapped with Ref. 119 Bang Case-control ACPA (+) or (−) RA; ACPA levels Smokers had a trend of higher ACPA levels than never-smokers without significant difference Significant interaction of CS with SE but not with *09:01 on ACPA (+) RA Never- or ever-smokers; SE; DRB1*09:01; ACPA 1924 RA cases and 1119 control subjects, Korea; partially overlapped with Ref. 115 Mahdi Intra case and case–control Anti-CEP-1 Ab response 43–63% of ACPA (+) cases were anti-CEP-1 Ab (+), and this subset was preferentially linked to HLA-DRB1*04. Combined effect of CS, PTPN22, and SE on anti-CEP (+) response Never- or ever-smokers; SE; PTPN22; ACPA; anti-CEP 1497 cases, Sweden and UK; 1000 cases and 872 controls, Sweden (cases were overlapped) Lundberg Case-control Specific ACPA responses The strongest association of SE, PTPN22, and CS for the RA subset anti-CEP-1 (+) or anti-cVim Ab (+) subsets of RA Never-, past, and current smokers; SE; PTPN22; ACPA subsets 1985 cases and 2252 matched controls, Sweden overlapped with Refs. 17, 121 Willemze intra-case Specific ACPA responses A significant interaction between CS and SE for the presence of ACPA, not restricted to specific citrullinated antigens Never- and ever-smokers; SE; ACPA subsets; RF; ANA 661 cases with recent onset (< 2 years), Netherland Fisher Case-control Specific ACPA responses, erosion CS-SE interaction was associated with all the ACPA (+) subgroups; highest OR in an anti-CCP (+) cVim (+) subset Never- and ever-smokers; SE and DRB1*09:01; ACPA subsets 513 cases and 1101 controls, Korea overlapped with Ref. 115 Kochi Case-control RA development PADI4 SNP (rs1748033) conferred a higher risk in men (OR 1.39) and in ever-smokers (OR 1.25) The highest risk in male ever-smokers (OR 1.46) Never- and ever-smokers; PADI4 SNP genotypes; gender; ACPA 1019 cases/907 controls and 999 cases/1128 controls, Japan; 635 cases/391 controls, Netherland
上記のように、関節リウマチと喫煙の関係がまとめられています。
男性は女性よりも喫煙の影響を受けやすいことが報告されています。また、喫煙は、疾患修飾性抗リウマチ薬(DMARDs)の治療効果に影響を与えるため、将来の変形のリスクにも関わってきます。
受動喫煙に関しては、小児期の受動喫煙が関節リウマチ発症への感受性に影響を及ぼすことを報告されとており、また疾患活動性は受動喫煙に影響される報告や、影響されない報告両方が出ています。
まとめ
関節リウマチ発症と喫煙についてまとめました。
タバコは関節リウマチの発症リスクを増やし、リウマチの抗体ができやすくなり、治療薬の効果を落としてしまう報告が数多く出ています。
関節リウマチが心配な方、関節リウマチの治療をはじめた方は、ぜひ禁煙しましょう。禁煙がなかなかできない、という場合には、禁煙外来などの方法もあります。御相談ください。
